Redis Watcher
The Redis Watcher tracks Redis operations in your NestJS application, monitoring commands, performance, and data access patterns.
What Gets Captured
- Redis command (get, set, del, etc.)
- Command arguments
- Execution duration
- Key pattern
- Operation status (success/error)
- Result data (truncated if large)
- Error messages
Configuration
NestLensModule.forRoot({
watchers: {
redis: {
enabled: true,
ignoreCommands: ['ping', 'info'],
maxResultSize: 1024, // 1KB
},
},
})
Configuration Options
| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | boolean | false | Enable/disable Redis tracking |
ignoreCommands | string[] | [] | Commands to ignore |
maxResultSize | number | 1024 | Max result size to capture (bytes) |
Payload Structure
interface RedisEntry {
type: 'redis';
payload: {
command: string; // Redis command
args: unknown[]; // Command arguments (masked if sensitive)
duration: number; // Execution time (ms)
keyPattern?: string; // Key pattern or name
status: 'success' | 'error';
result?: unknown; // Command result (masked if sensitive)
error?: string; // Error message
};
}
Usage Example
Setup Redis Client
// Install: npm install redis
import { createClient } from 'redis';
@Module({
providers: [
{
provide: 'REDIS_CLIENT',
useFactory: async () => {
const client = createClient({
url: 'redis://localhost:6379',
});
await client.connect();
return client;
},
},
],
})
export class AppModule {}
Provide Redis Client to NestLens
import { NESTLENS_REDIS_CLIENT } from 'nestlens';
@Module({
providers: [
{
provide: NESTLENS_REDIS_CLIENT,
useExisting: 'REDIS_CLIENT',
},
],
})
export class AppModule {}
Using Redis
import { Injectable, Inject } from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class CacheService {
constructor(
@Inject('REDIS_CLIENT') private redis: RedisClient,
) {}
async get(key: string): Promise<string | null> {
// Automatically tracked
return await this.redis.get(key);
}
async set(key: string, value: string, ttl?: number): Promise<void> {
if (ttl) {
await this.redis.setEx(key, ttl, value);
} else {
await this.redis.set(key, value);
}
}
async delete(key: string): Promise<void> {
await this.redis.del(key);
}
async increment(key: string): Promise<number> {
return await this.redis.incr(key);
}
}
Dashboard View
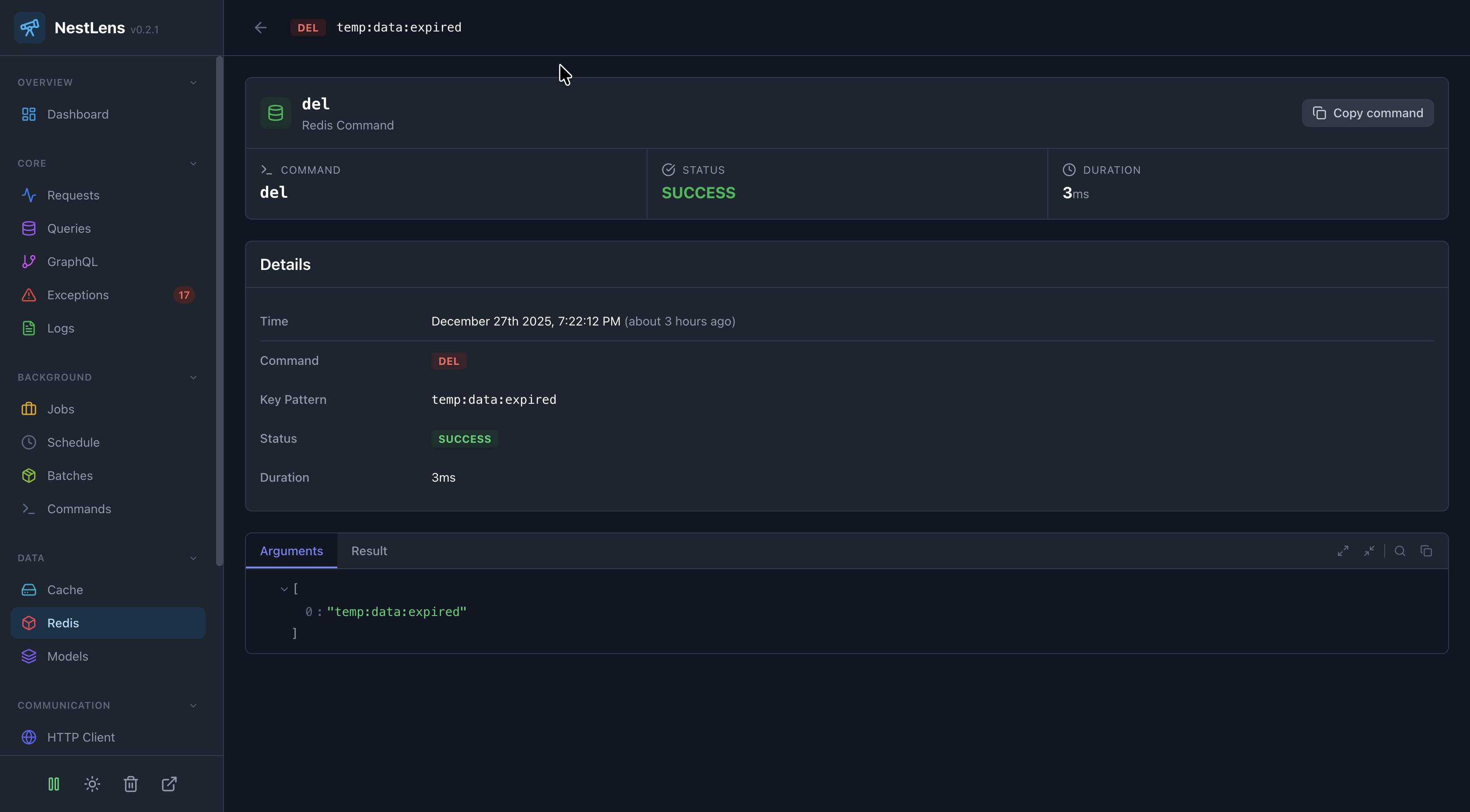
In the NestLens dashboard, Redis entries show:
- Command execution timeline
- Most used commands
- Slow commands
- Key access patterns
- Error rates
- Cache hit/miss analysis (for GET commands)
Sensitive Key Masking
Keys containing sensitive patterns are automatically masked:
passwordtokensecretauthkeycredentialsession
// Values are masked in dashboard
await redis.set('user:123:token', 'secret-token'); // Masked
await redis.set('session:abc123', 'session-data'); // Masked
await redis.set('user:123:name', 'John'); // Not masked
Common Redis Patterns
Caching
async getCachedData(key: string): Promise<any> {
const cached = await this.redis.get(key);
if (cached) return JSON.parse(cached);
const data = await this.fetchData();
await this.redis.setEx(key, 3600, JSON.stringify(data));
return data;
}
Rate Limiting
async checkRateLimit(userId: string): Promise<boolean> {
const key = `rate-limit:${userId}`;
const count = await this.redis.incr(key);
if (count === 1) {
await this.redis.expire(key, 60); // 1 minute window
}
return count <= 100; // Max 100 requests per minute
}
Pub/Sub
async publishEvent(channel: string, message: string) {
await this.redis.publish(channel, message);
}
async subscribe(channel: string, handler: (message: string) => void) {
const subscriber = this.redis.duplicate();
await subscriber.connect();
await subscriber.subscribe(channel, handler);
}
Related Watchers
- Cache Watcher - Track higher-level cache operations
- Request Watcher - See Redis commands per request